CentOS7 をネットワークインストールする。その1 VMware
で、VMwareにCentOS7を入れてPXEサーバーをたて、そこから別のマシンにCentOSをネットワークインストールすることにしました。
CentOS7 をネットワークインストールする。その2 PXEサーバ
CentOS7 をネットワークインストールする。その3 xinetd ではなく systemd を
初めは Xinetd を使ったのですがうまくインストールすることができなかったのでSystemd を使うことにしました。ほぼ下記の記事の通りに進めています。
nothen.com.ar
VMwareに入れたCentOS7のターミナルを開きます。
1. Install the necessary packages:
# yum install syslinux tftp-server
インストール:
syslinux.x86_64 0:4.05-12.el7 tftp-server.x86_64 0:5.2-12.el7
完了しました!
Note that even though Xinetd will be installed as a dependency, both the Xinetd “super-service” and the tftp Xinetd “sub-service” will be disabled:
# systemctl disable xinetd.service
rm '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/xinetd.service'
Xinetdが既にインストールされてしまっている環境の方は、上記のようにXinetdを「無効」にしてください。
私は今回すっからかんのVmware上のCentOS7からスタートしてますのでXinetdは入っていません。Xinetd がちゃんと無効になっているかだけ調べます。
# grep disable /etc/xinetd.d/tftp
disable = yes
2. On the other hand, the tftp socket on Systemd will be enabled and listening.
# systemctl status tftp.socket
● tftp.socket - Tftp Server Activation Socket
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/tftp.socket; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Listen: [::]:69 (Datagram)
# systemctl start tftp.socket
# systemctl status tftp.socket
● tftp.socket - Tftp Server Activation Socket
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/tftp.socket; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (listening) since 日 2016-04-16 16:16:24 JST; 2s ago
Listen: [::]:69 (Datagram)
4月 16 16:16:24 tako systemd[1]: Listening on Tftp Server Activation Socket.
4月 16 16:16:24 tako systemd[1]: Starting Tftp Server Activation Socket.
# systemctl enable tftp.socket
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/sockets.target.wants/tftp.socket to /usr/lib/systemd/system/tftp.socket.
# systemctl status tftp.socket
● tftp.socket - Tftp Server Activation Socket
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/tftp.socket; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (listening) since 日 2016-04-16 16:16:24 JST; 39s ago
Listen: [::]:69 (Datagram)
4月 16 16:16:24 tako systemd[1]: Listening on Tftp Server Activation Socket.
4月 16 16:16:24 tako systemd[1]: Starting Tftp Server Activation Socket.
次にFireWallを止めます。CentOS6までは iptables を使っていましたが、CentOS7からは firewalld になりました。
Since firewalld is active, I’ll add the tftp port on the appropriate zone:
# firewall-cmd --add-service=tftp --zone=internal --permanent
success
# firewall-cmd --reload
success
参考ページでは上記の通り、FireWall有効のまま設定していたのですが私はこの通りにしてもうまくいかず、PXEからのブート時に
PXE-32: TFTP open timeout
と表示されその先に進めませんでした。
http://itdoc.hitachi.co.jp/manuals/3020/30203L5360/SCDM0220.HTM
Q8
ネットワークブート中,クライアント画面に以下のメッセージが表示され,シナリオ実行エラーとなる。
PXE-E32: TFTP open timeout
A8
Windowsファイアウォールやセキュリティ対策ソフトウェアなどのポートブロック機能によって,TFTPポート(ポート番号:69)がブロックされている可能性があります。
そこでfirewallは「停止」することにしました。PXEサーバは一時的な利用でお役御免ですので、まあいいかなと。
# systemctl status firewalld
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since 日 2016-04-16 16:12:32 JST; 16min ago
Main PID: 900 (firewalld)
CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service
└─900 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid
4月 16 16:12:24 tako systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...
4月 16 16:12:32 tako systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.
# systemctl disable firewalld
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/basic.target.wants/firewalld.service.
# systemctl status firewalld
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since 日 2016-04-16 16:12:32 JST; 17min ago
Main PID: 900 (firewalld)
CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service
└─900 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid
4月 16 16:12:24 tako systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...
4月 16 16:12:32 tako systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.
# systemctl stop firewalld
# systemctl status firewalld
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
4月 16 16:12:24 tako systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...
4月 16 16:12:32 tako systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.
4月 16 16:30:33 tako systemd[1]: Stopping firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...
4月 16 16:30:35 tako systemd[1]: Stopped firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.
# vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux
SELINUX=enforcing から SELINUX=disabled に変更。
3. When PXE booting, the server needs to send the client some basic files, which are provided by the syslinux package that I installed on the first step. Then needs to send the kernel and the initial ramdisk matching the target operating system, (just CentOS7 in this case), which I can get from the OS iso, or manually getting the files from the public repository:
現在 /var/lib/tftpboot/ は空です。
# ls /var/lib/tftpboot/
ここに /usr/share/syslinux/ より必要なファイルをコピーします。
# cd /var/lib/tftpboot
[root@tako tftpboot]# cp /usr/share/syslinux/{pxelinux.0,vesamenu.c32} .
[root@tako tftpboot]# ls
pxelinux.0 vesamenu.c32
wget -q
http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7.1.1503/os/x86_64/isolinux/{vmlinuz,initrd.img,splash.png}
(このディレクトリは現在使われていません)
(注:今回は下記の通り北陸先端大(JAIST)を使いました。また私のインストール先PCのCPUが古いAMD製(Opteron)のためか、CentOS7.2がインストールできなかった(rest_init+0x80/0x80で止まる)のでCentOS7.1をインストールしました。
0009860: 3.10.0-327.el7 crashes on boot - CentOS Bug Tracker
『Steps To Reproduce Reboot an affected AMD System』
CentOS7.1 http://vault.centos.org/7.1.1503/os/x86_64/
ブート画面で文字がずらずら流れていき、dracut-intqueue うんぬんで数分以上ほぼ同じ文言を繰り替えしてるからちゃんと動いてるのか心配だったけどなんとか「CentOS7へようこそ」へ進めた。ただ、7.2にバージョンアップすると私の環境では止まります…。
適宜自分の欲しいバージョンに変更してください。数字だけ変えてもディレクトリがない場合や、splash.jpg が splash.png だったりと差異がありますので実際に見に行って確認してからアドレスを設定しましょう。)
以下 CentOS7.2を例にとって進めます。
[root@tako tftpboot]# wget http://ftp.jaist.ac.jp/pub/Linux/CentOS/7.2.1511/os/x86_64/isolinux/{vmlinuz,initrd.img,splash.png}
[root@tako tftpboot]# ls
initrd.img pxelinux.0 splash.png vesamenu.c32 vmlinuz
4. I will now create a menu for my PXE service, that will have entries for two different deployment methods: an automated one using a kickstart, and a manual one using a public repository (assuming of course that the client has access to internet). Then I’ll add a third entry for booting from hard drive:
Kickstartファイルを作って自動インストールする方がスマートですが、私はまだ知識がないので手動でいきます。
[root@tako tftpboot]# mkdir pxelinux.cfg
[root@tako tftpboot]# ls
initrd.img pxelinux.0 pxelinux.cfg splash.jpg vesamenu.c32 vmlinuz
[root@tako tftpboot]# cd pxelinux.cfg/
[root@tako pxelinux.cfg]# pwd
/var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
[root@tako pxelinux.cfg]# vi default
default vesamenu.c32
timeout 200
menu background splash.jpg ←pngの場合は変更を。
ontimeout local
label repo
menu label ^Install CentOS without Kickstart
kernel vmlinuz
append initrd=initrd.img ip=dhcp ksdevice=link repo=http://ftp.jaist.ac.jp/pub/Linux/CentOS/7.2.1511/os/x86_64/
label local
menu label Boot from Hard Drive
localboot 0xffff
[root@tako pxelinux.cfg]# cd ~
[root@tako ~]#
5. And finally, for a server to be able to use the PXE service, the DHCP server (which could be on the same PXE server or on a different one) needs to know which is the “next-server”, and what file to provide to get the environment started. Something like “go to this guy and get this”. You do that by adding these two lines in red on dhcpd.conf:
このあと cat /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf とDHCPの設定に入るのですが、私はまだDHCPをインストールしていませんのでここで入れます。
[root@tako ~]# rpm -qa | grep dhcp
dhcp-libs-4.2.5-42.el7.centos.x86_64
dhcp-common-4.2.5-42.el7.centos.x86_64
[root@tako pxelinux.cfg]# ls /etc/dhcp/
dhclient.d
[root@tako ~]# yum install dhcp
インストール:
dhcp.x86_64 12:4.2.5-42.el7.centos
完了しました!
[root@tako pxelinux.cfg]# rpm -qa | grep dhcp
dhcp-libs-4.2.5-42.el7.centos.x86_64
dhcp-4.2.5-42.el7.centos.x86_64
dhcp-common-4.2.5-42.el7.centos.x86_64
[root@tako ~]# ls /etc/dhcp/
dhclient.d dhcpd.conf dhcpd6.conf
DHCPの設定。
[root@tako ~]# vi /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
allow unknown-clients;
option domain-name-servers 192.168.10.1;
authoritative;(←これの記載を忘れて途中で止まったことがあります。しかし再現できず)
subnet 192.168.10.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers 192.168.10.1;
range 192.168.10.2 192.168.10.20;
next-server 192.168.10.2; (←VMWare上のipアドレス)
filename "pxelinux.0";
}
CentOS7から ifconfig が非推奨となりました。よって ip コマンドで。
[root@tako ~]# ip addr (または ip a)
~
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc
fifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:24:0b:d1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.10.2/24 brd 192.168.10.255 scope global eth0
~
DHCPを起動。
[root@tako ~]# systemctl status dhcpd.service
● dhcpd.service - DHCPv4 Server Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/dhcpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:dhcpd(8)
man:dhcpd.conf(5)
[root@tako ~]# systemctl enable dhcpd.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/dhcpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/dhcpd.service.
[root@tako ~]# systemctl start dhcpd.service
[root@tako ~]# systemctl status dhcpd.service
● dhcpd.service - DHCPv4 Server Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/dhcpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 日 2016-04-16 15:42:25 JST; 4s ago
Docs: man:dhcpd(8)
man:dhcpd.conf(5)
Main PID: 5680 (dhcpd)
Status: "Dispatching packets..."
CGroup: /system.slice/dhcpd.service
└─5680 /usr/sbin/dhcpd -f -cf /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf -user dhcpd -gr...
4月 16 15:42:25 tako dhcpd[5680]: No subnet declaration for virbr0 (192.1...).
4月 16 15:42:25 tako dhcpd[5680]: ** Ignoring requests on virbr0. If thi...at
4月 16 15:42:25 tako dhcpd[5680]: you want, please write a subnet decl...on
4月 16 15:42:25 tako dhcpd[5680]: in your dhcpd.conf file for the netw...nt
4月 16 15:42:25 tako dhcpd[5680]: to which interface virbr0 is attached. **
4月 16 15:42:25 tako dhcpd[5680]:
(何か出たけど仮想ネットワークのNICの話なので今回は無視する↑)
4月 16 15:42:25 tako dhcpd[5680]: Listening on LPF/eth0/00:0c:29:58:ca:32...24
4月 16 15:42:25 tako dhcpd[5680]: Sending on LPF/eth0/00:0c:29:58:ca:32...24
4月 16 15:42:25 tako dhcpd[5680]: Sending on Socket/fallback/fallback-net
4月 16 15:42:25 tako systemd[1]: Started DHCPv4 Server Daemon.
Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
That’s all in regards to configuring PXE. When I complete the steps above, the file structure will look like this:
ここまでがPXEの設定です。上記手順を終えると、ファイル構成は下記の8個になります。
root@tako ~]# find /var/lib/tftpboot/
/var/lib/tftpboot/
/var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.0
/var/lib/tftpboot/vesamenu.c32
/var/lib/tftpboot/vmlinuz
/var/lib/tftpboot/initrd.img
/var/lib/tftpboot/splash.jpg
/var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
/var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
Additionally, since I’m not using Xinetd now, if I wanted to modify the service startup parameters, I no longer modify /etc/xinetd.d/tftp, but the corresponding Systemd file instead. I recommend making a copy of the original file to /etc/systemd/system (takes precedence over /usr/lib/systemd/system) so that future updates don’t overwrite the customized file.
Xinetdは使っていないので、サービスのスタートアップパラメーターを設定する際も、もう /etc/xinetd.d/tftp は使いません。Systemdファイルが代わりを務めます。
設定ファイルは、/usr/lib/systemd/system/以下と/etc/systemd/system/以下にあります。両方のディレクトリに同名の設定ファイルがある場合は、後者(/etc/systemd/system/)のファイルが優先されます。前者(/usr/lib/systemd/system/)には、RPMパッケージが提供するシステム標準の設定を配置しておき、システム管理者が設定変更する場合は、後者にファイルをコピーした上で修正を加えます。
Systemd入門(4) - serviceタイプUnitの設定ファイル - めもめも
設定ファイルの確認・コピー。
[root@tako ~]# ls /usr/lib/systemd/system/
~
teamd@.service
tftp.service
tftp.socket
~
[root@tako ~]# ls /etc/systemd/system
~
sysinit.target.wants
system-update.target.wants
[root@tako ~]# cp /usr/lib/systemd/system/tftp.service /etc/systemd/system
[root@tako ~]# ls /etc/systemd/system
~
sysinit.target.wants
system-update.target.wants
tftp.service
For example, to increase verbosity for this service, I add “-vvv” on the line that indicates the executable command (ExecStart):
設定の例として、サービスの冗長性を上げます。-vvv をサービス起動コマンドを示すExecStartライン上に付け加えました。
[root@tako ~]# vi /etc/systemd/system/tftp.service
[Unit]
Description=Tftp Server
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/in.tftpd -vvv -s /var/lib/tftpboot
StandardInput=socket
/etc/systemd/system/以下の「systemdとしてのservice設定ファイル」を変更した場合、この変更をsystemdに反映させるには、次のdaemon-reloadオプションを使用します。
Systemd入門(2) - Serviceの操作方法 - めもめも
[root@tako ~]# systemctl daemon-reload
Then, watching journalctl while a client boots on PXE, it shows detailed information of the process:
[root@tako ~]# journalctl -f -n0
この後、インストール先のPCを立ち上げ、途中でF12キーなどを押しPXEブートに入る。
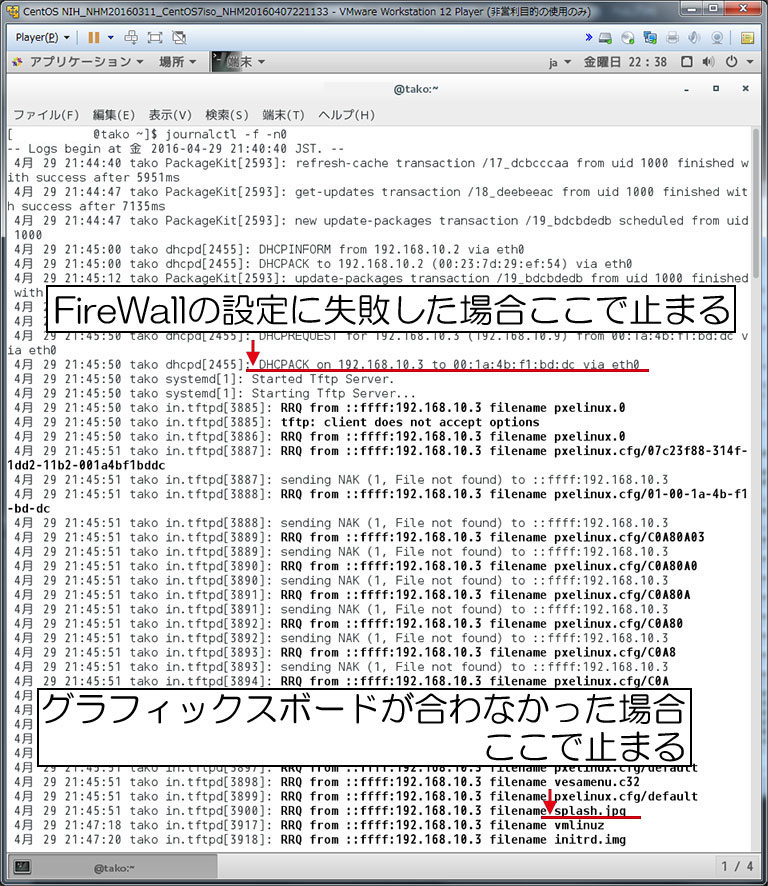
CentOS7のスプラッシュ画面まで行ったが、その先に進もうとするとアンダーバー一本で止まってしまった。確かにログも
4月 16 16:41:50 tako in.tftpd[6388]: RRQ from ::ffff:192.168.10.3 filename splash.jpg
で止まっており、その先に進めていない。
毎度引っかかるグラフィックボードが悪いんだろうなと予想し検索したら実際そのようでした。
スプラッシュ画面で[Tab]を押してオプションを追加。
vmlinux initrd.img initrd=initrd.img ip=dhcp ksdevice=link repo=http://ftp.jaist.ac.jp/pub/Linux/CentOS/6.7/os/x86_64/ に続けて
xdriver=vesa nomodeset と記載することでその先に進めた。
追記:DHCPの設定を間違っても(next-server の値を間違ったり)上記のDHCPACKあたりで止まります。修正してDHCPを再起動してもう一度試してください。
追記:後日 VMware vSphere Hypervisor で仮想化してみました。こっちの方が後で楽そうでいいですね。
ML115 G1 に VMware vSphere Hypervisor をインストール - demandosigno
ただ、vSphereはGeforceグラボがパススルー対応外のようで、結局生インストールに戻しました。
